Molecular Signaling
-
Narayana Netralaya Foundation > Molecular Signaling
Molecular Signaling
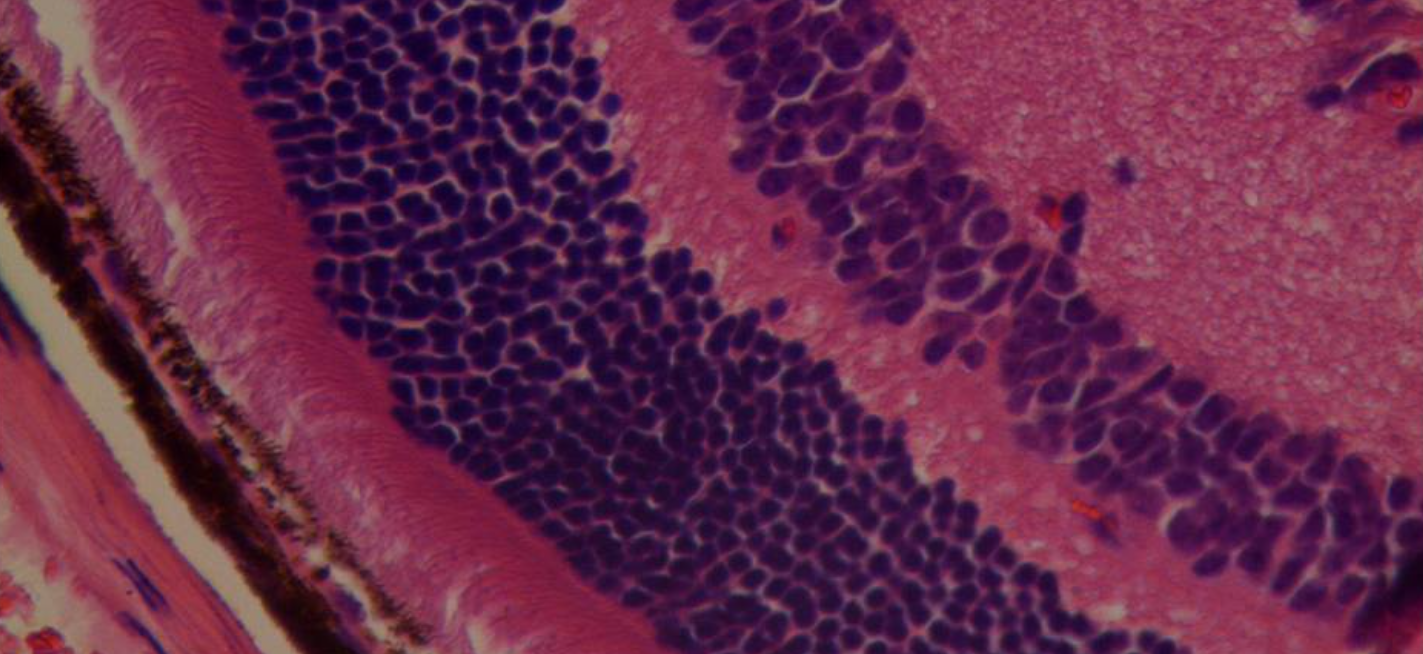
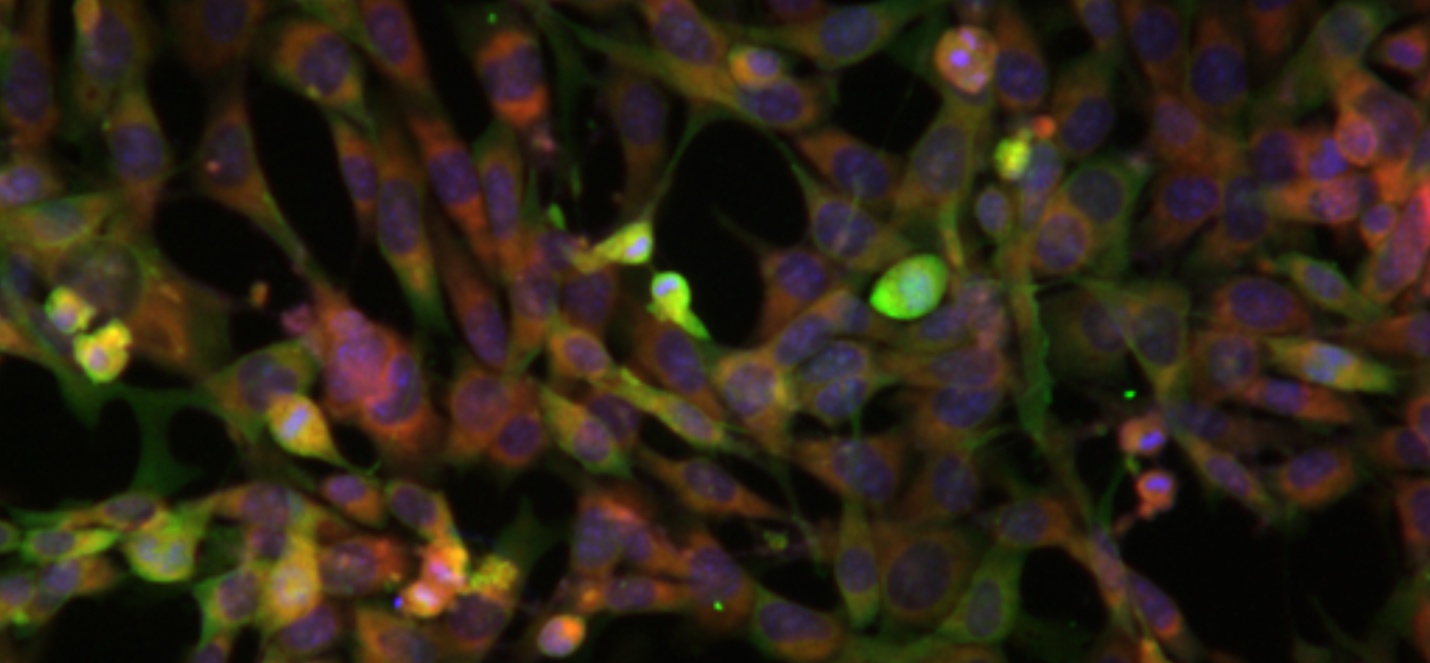
Cell signaling/communication is the basis for other vital/essential cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, inflammation, autophagy, vascularisation, metabolism, etc. Cells not only interact with their immediate microenvironment, and also respond to signals that originate much further away. Molecules carrying the message or signals are called ligands, these molecules attach to the specific receptor which might be present in the cell surface, cytosol, or the nucleus. The ligand/receptor interaction leads to the activation of signaling pathways. Cell/ molecular signaling is mainly autocrine, endocrine, paracrine, and Juxtacrine. Signaling pathways may be classified according to the source of a signaling molecule or ligand. We at GROW lab work at understanding the regulation and the mechanism of how various molecular signaling pathways are associated with the pathogenesis of Ocular Disease. Further, we aim to identify novel therapeutic approaches to targeting the signaling pathways which are associated with disease progression. Understating the regulation of the NFKB pathway to modulate inflammation associated with the pathogenesis of several ocular diseases including Keratoconus, Dry eyes, AMD, DR, glaucoma, etc. modulation of NFKB/AKT/MAPKinases under chronic stress might help us develop novel alternate therapeutic approaches towards inflammation associated ocular diseases. Extracellular stresses like oxidative stress, UVB rays, starvation, and other stressors lead to the activation of autophagy. Autophagy is a conserved molecular mechanism essential for the clearance of cellular wastes. Modulation of autophagy using activators and inhibitors which are mTOR independent or mTOR dependent helps novel target approach towards KC, dry eyes, pterygium, AMD, and other chronic diseases. The Autophagy pathway is mainly regulated through AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway.
we also work on other diverse signaling networks such as: SMAD signaling pathway which is associated with fibrosis and wound healing, Crosstalk between Aquaporins and WNT signaling in Glaucoma, ICAM1 and angiogenin in DR and AMD, and miRNA’s- Investigation of miRNA 182-5p and miRNA221-3p in angiogenesis and hyperglycemia.
Ocular Cancer– multi-omics approach towards retinoblastoma- transcriptomics, metabolomic analysis of retinoblastoma tissues and vitreous samples. understanding the signaling pathways associated with Retinoblastoma progression.
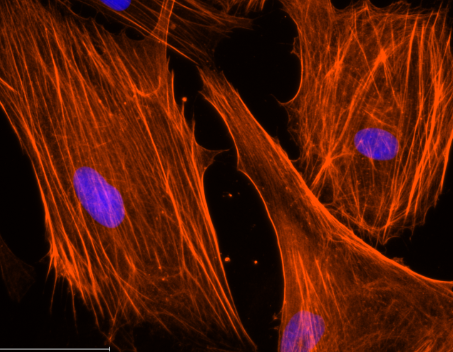
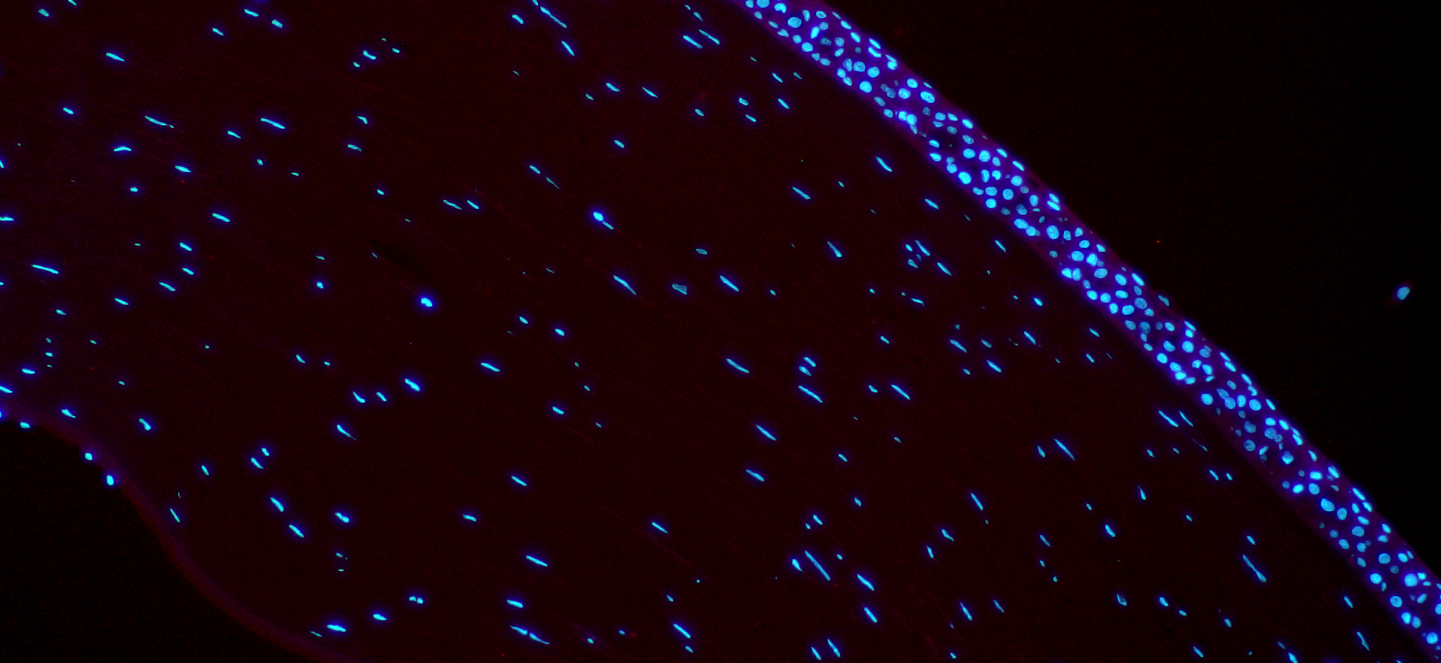
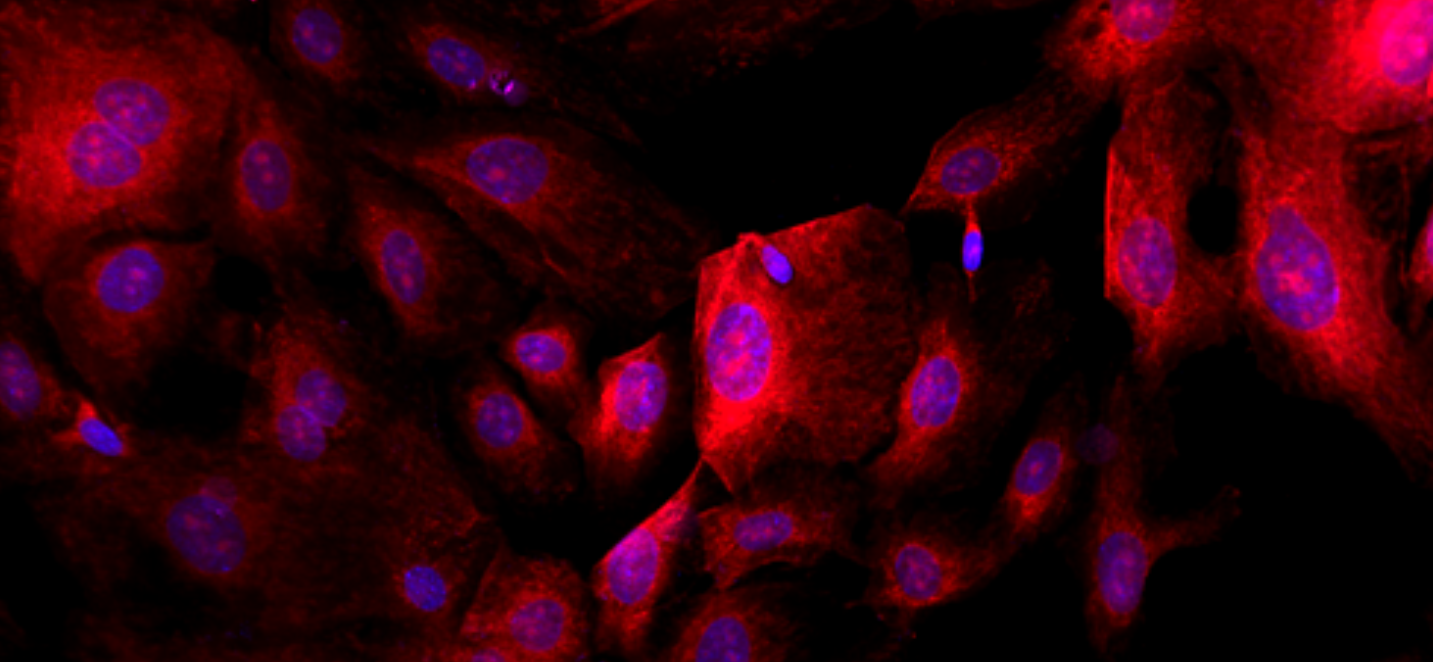
Alpha-Sma staining of Human Corneal Fibroblast
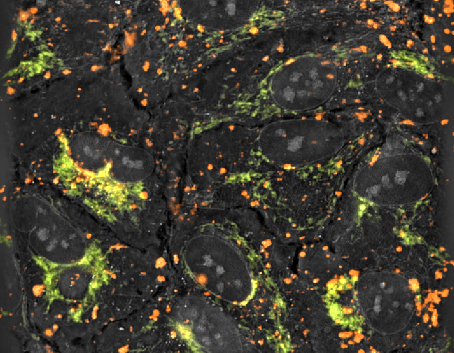
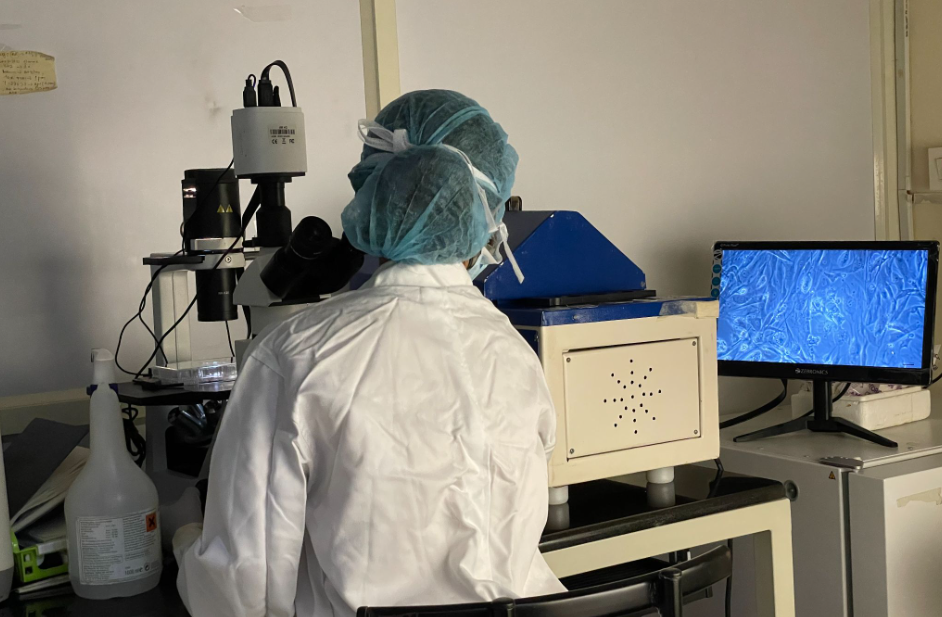
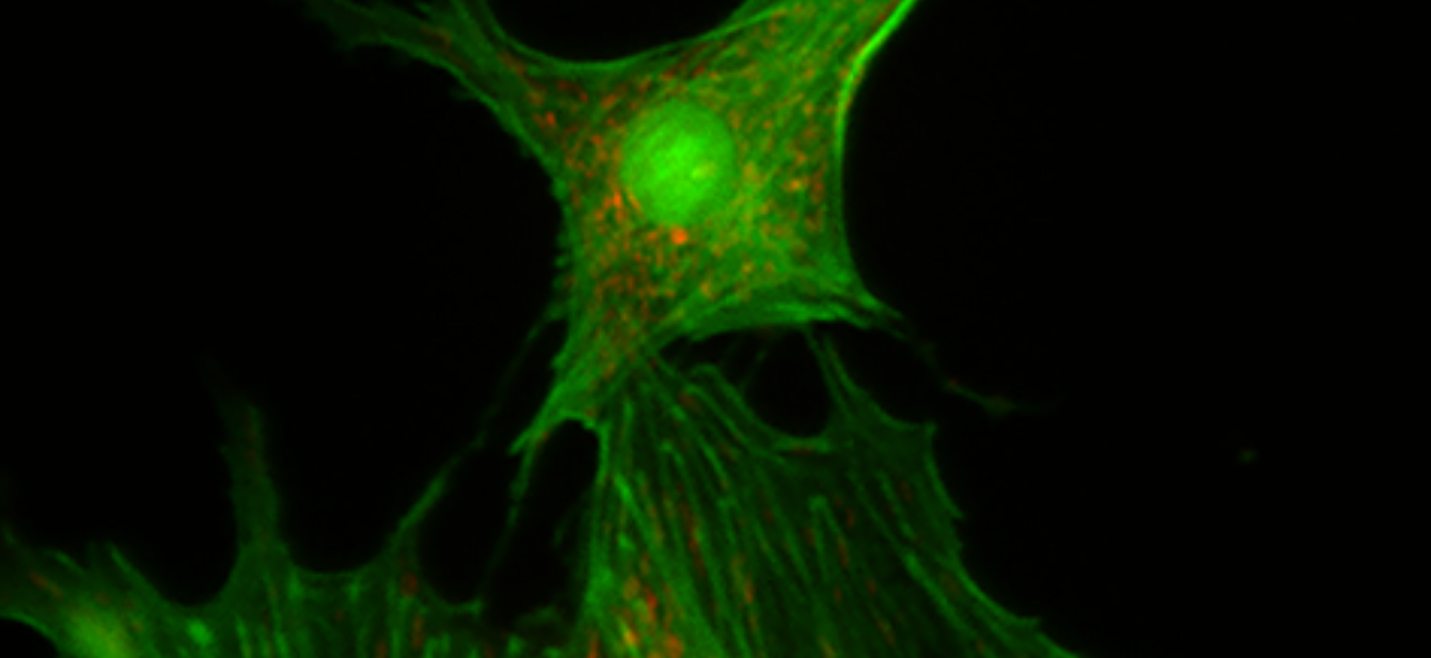
Live imaging of ARPE19 cells